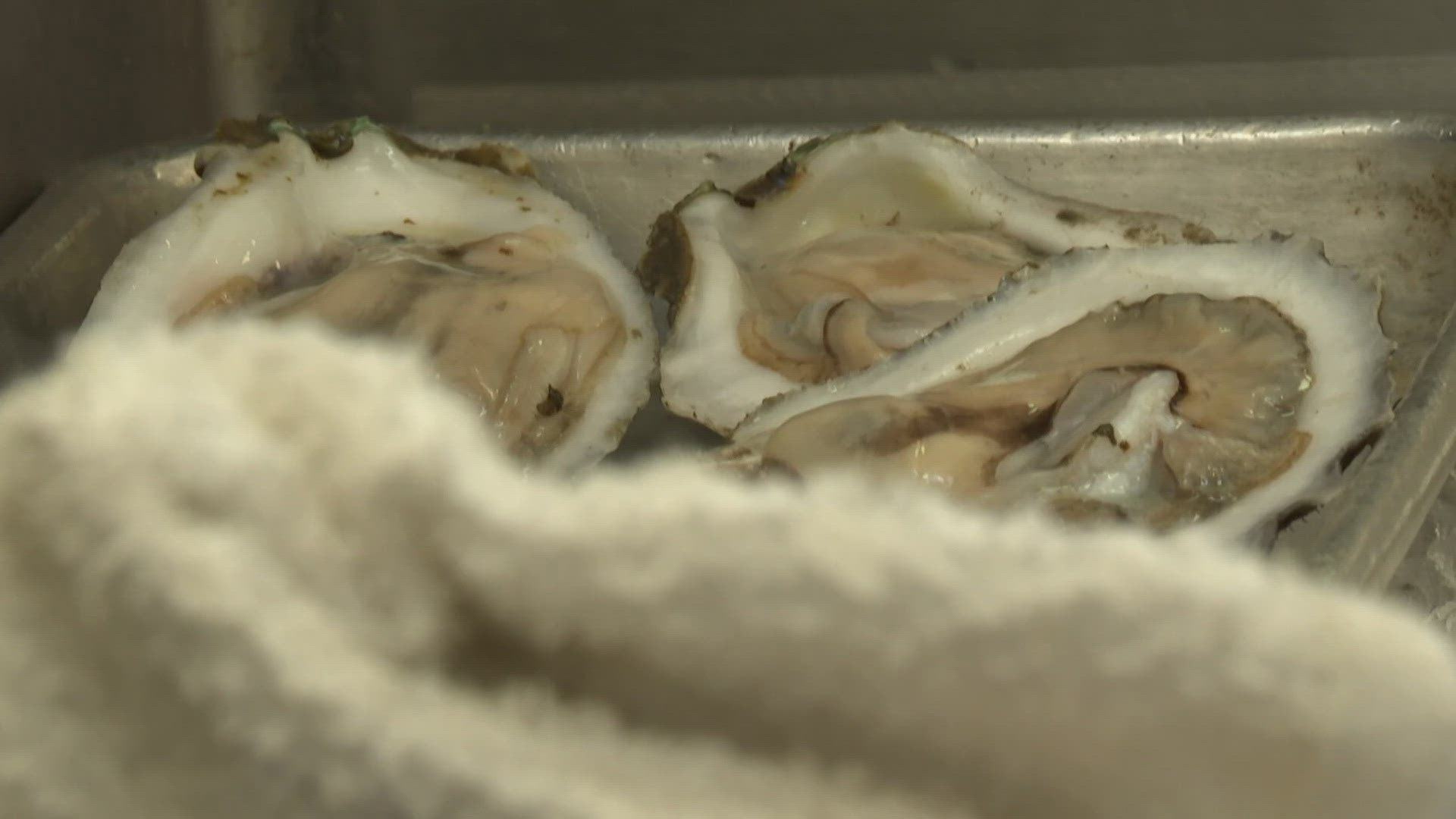
El consumo de marisco crudo ha sido durante mucho tiempo un manjar valorado en varias regiones del mundo; sin embargo, eventos recientes han resaltado nuevamente los peligros que pueden estar ligados a esta práctica. Las autoridades sanitarias han confirmado que dos personas fallecieron tras consumir ostras crudas contaminadas con una peligrosa cepa de bacteria carnívora. Estos incidentes son un recordatorio claro de los posibles riesgos para la salud vinculados al consumo de mariscos sin cocción, especialmente cuando no se toman las precauciones adecuadas de manejo y almacenamiento.
According to officials, the victims consumed the raw oysters at different locations, yet both cases shared a similar outcome. Each person became gravely ill shortly after the meal, and despite receiving medical treatment, neither was able to recover from the severe infection. The bacteria responsible for these fatalities is known for its rapid progression and ability to cause life-threatening complications within hours of exposure.
Healthcare professionals have discovered that the pathogen is Vibrio vulnificus, a bacterium that naturally thrives in warm oceanic waters. Although the presence of this microorganism is not rare in marine habitats, infections in people are infrequent. Nonetheless, when such infections do develop, they can be highly severe, particularly for those with compromised immune systems or pre-existing medical conditions. The bacterium can invade the bloodstream and prompt sepsis, resulting in a significant fatality rate if not promptly managed.
Health officials have stressed that the danger does not come from all oysters, but rather from those that have been harvested from waters where Vibrio bacteria thrive. These bacteria multiply in warm temperatures, making the summer and early fall months particularly risky for consuming raw shellfish. In most cases, proper cooking kills the bacteria and eliminates the threat, which is why experts strongly advise against eating raw or undercooked seafood during these times of the year.
The recent fatalities have sparked renewed debates concerning food safety standards and the significance of consumer education. Despite a common belief among seafood lovers that consuming raw oysters is safe if sourced from trusted vendors, it’s important to note that even shellfish taken from observed locations might contain dangerous microorganisms. Health authorities advise that eateries and seafood outlets adhere to rigorous handling protocols, such as maintaining shellfish at correct refrigeration levels and preventing cross-contamination.
Aside from food management, there is a growing emphasis on individuals being aware of their personal risk factors before eating raw shellfish. Those with liver conditions, diabetes, or weakened immune defenses are especially susceptible to Vibrio infections. For these individuals, even minimal contact with the bacteria can result in severe health repercussions. Medical professionals advise people at high risk to completely refrain from consuming raw oysters, regardless of their freshness or perceived quality.
Symptoms of Vibrio infection typically begin within 24 to 48 hours after ingestion and can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. In more severe cases, the infection can progress rapidly, causing blistering skin lesions, tissue necrosis, and septic shock. This is why immediate medical attention is crucial if someone develops these symptoms after eating raw seafood. Early treatment with powerful antibiotics can sometimes save lives, but delays in seeking care can be fatal.
Health agencies in various states are conducting inquiries to identify the origin of the tainted oysters associated with these incidents. Authorities are collaborating with both suppliers and distributors to determine the source of the seafood and to avert additional health issues. In the meantime, the public has been alerted, advising individuals to be vigilant and to think about cooking oysters completely prior to eating.
Certain specialists propose stricter labeling standards for uncooked seafood items. Labels that explicitly detail the dangers of consuming raw oysters, akin to the cautionary messages on cigarette packs, might contribute to decreasing the annual infection rates. Meanwhile, some support implementing seasonal bans on the sale of raw oysters during the hottest months, a period when Vibrio bacteria are most abundant in coastal environments.
While these tragic deaths are relatively rare compared to the millions of servings of oysters consumed annually, they underscore the importance of understanding the risks associated with raw seafood. For many, the allure of fresh, raw oysters may seem worth the gamble, but as these cases illustrate, the consequences can be severe and irreversible. Public health officials hope that by sharing these warnings and reinforcing safe food practices, future tragedies can be prevented.
Responsibility for ensuring safety is shared among various entities: suppliers are required to maintain adequate harvesting and storage practices, dining establishments are obligated to adhere to strict sanitation standards, and individuals must be conscious about their dietary selections. Properly cooking oysters is the most dependable method to eradicate dangerous bacteria, allowing people to enjoy them without the worry of illness.
These recent cases serve as a powerful reminder that while raw seafood may be a culinary tradition, it carries inherent dangers that should never be underestimated. With the right precautions and awareness, it is possible to enjoy seafood without putting health and lives at risk. For those who value safety over tradition, a simple decision—to cook rather than consume raw—could make all the difference.